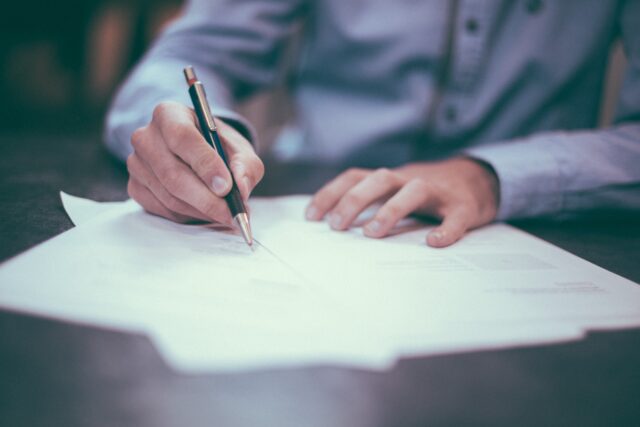
In the Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM), employment regulations are dealt with by the provisions of ADGM Employment Regulations 2019 (the “Regulations”), ADGM Employment Regulations (Engaging Non-Employees) Rules 2023 (the “Rules of 2023”), and ADGM Employment Regulations 2019 (Compensation Awards and Limits) Rules 2019 (the “Rules of 2019”). The usual practice is to develop an in-house employment handbook giving the details of the respective company, their responsibilities, conditions of employment, and the obligations of employers and employees towards the company.
This article lists three major categories of records that must be maintained by companies and employees:
- Business-related records to be maintained by the employer;
- Employee-related records to be maintained by the employer; and
- Records to be maintained by the employee.
Business-related records to be maintained by the employer:
- Business License: A valid business license issued by the ADGM authorities, such as the ADGM Registration Authority, is required to operate within the ADGM jurisdiction. Without a valid business license, a company cannot exist.
- Personal documents of the employer: ADGM being a free zone jurisdiction, might require the personal documents of the employer such as the passport, EID, Unified ID, etc., If the employer is unavailable in the country during the recruitment process, there are situations where the personal documents of the Authorized Signatory of the employer or the manager of the employer’s business are required.
- Memorandum and Articles of Association: The employer may need to submit the Memorandum and Articles of Association of the company, to the relevant authorities of the ADGM, as and when the requirement arises. However, this is not a mandatory requirement when recruiting an employee in the ADGM.
- Employment Contracts: Employers are generally required to have written employment contracts with their employees. These contracts should outline the terms and conditions of employment, such as job responsibilities, probation, remuneration, working hours, leave entitlements, termination, jurisdiction and relevant legal provisions along with other relevant provisions that are usually essential for an employment contract to be binding and valid.
- Employee Handbook: It is advisable for employers to have an employee handbook or manual that provides information about the policy of the company, rules based on which the company is operational, and procedures outlining how to conduct and handle any adverse situation, and in any circumstances. It is not mandatory to have an employee handbook. However, having an employee handbook helps to set clear expectations and guidelines for employees during their course of employment in the company.
- Financial Records: Employers are always required to maintain the financial records of the company, including accounting books, bank statements, payroll records, and tax-related documents, as per the applicable regulations. It is advisable to have yearly auditing for all the employers in order to analyze the status of the company. This helps in recruitment wherein these financial records would outline the financial stability of the company to pay the required remuneration to the employees.
Employee-related records to be maintained by the employer
In ADGM, unlike in the mainland and other free zones, there are no such specific document requirements. However, usually, the ADGM authorities require the employer to maintain a record of information on each employee.
For each employee, the employer shall keep records of the following information:
- a copy of the Employee’s Contract of Employment;
- name, date of birth, occupation details, contact details of the employee – both residential and postal address;
- employment commencement date of the employee;
- details of the wage / salary / remuneration given to the employees, both gross and net salary details;
- applicable pay period;
- working hours of the employee in accordance with the contract, which is mutually agreed upon between the employer and the employees;
- any additional benefits paid by the employer to the employee;
- any deduction made by the employer from the wages of the employee, and its reasons;
- National holidays availed by the employee and the payment made by the employer;
- the dates on which the employee has taken annual leave or vacation, the amount paid by the employer, the outstanding amount that is due to be paid to the employee;
- any other leave that is availed by the employee, and the payment made by the employer for such leave that is availed by the employee;
- the amount payable / paid to the employee by way of end-of-service gratuity and any other severance payment paid to the employee on termination of employment duration.
The above-mentioned records of the employee shall be maintained by the employer:
- For a minimum of two years after the termination of the employment of the employee;
- In the English language;
- In electronic format or hard copy format.
Records to be maintained by the employees
- Passport: Employees working in ADGM or a proposed employee should have a valid passport and that must be submitted as proof when required. An employee must have a passport that is valid for at least six (6) months and be between the ages of eighteen (18) and sixty (60). However, the age group is not a mandatory requirement. This is the usual age group that is actively being recruited in the ADGM.
- Visa: Employees working in ADGM are typically required to have, along with a valid passport, an appropriate work visa or a residency permit that is issued by the relevant UAE authorities, such as the General Directorate of Residency and Foreigners Affairs (GDRFA), or the Federal Citizenship Authorities. It is usually the responsibility and the obligation of the employer to take the work permit and visa as relevant, for their respective employee.
- Emirates ID Card: UAE nationals and residents are generally required to obtain an Emirates ID card, which serves as an identification document within the country.
- Educational and Professional Certificates: Depending upon the industry and job role, employees must provide their educational certificates, and professional qualifications to demonstrate their eligibility for employment. These certificates are not mandatory in all the job profiles; however, it is important to have these certificates.
The educational and professional certificates certified as true copies by the Notary Public in the country of origin of the expatriate employees, legalized by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA attestation) in the country of origin of the expatriate employees, and legalized by the United Arab Emirates Embassy in the country of origin of the expatriate employees. Once the Legalization and Attestation process is completed in the home country of the expatriate employees, then the documents will have to be legalized in the UAE by affixing the stamp of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA) and Ministry of Law and Justice (MOJ). These documents or certificates further need to be duly translated into Arabic. However, in ADGM, as of today, there is no such mandatory requirement which states that an employee needs to get the educational and professional certificates to be legalized and notarized. But it is recommended widely to keep the legalized and attested educational and professional certificates ready.
- Bank Account Details: Employees may be required to provide their bank account details for salary purposes, as most of the employers prefer to transfer salaries electronically. However, there is a scheme in UAE, generally, to have a company bank account exclusively for employment purposes and for the purpose of managing the remuneration for the employees. Through this method, the employer would create another bank account, apart from their personal bank account, for the employee so that once the probation of the employee is confirmed, salary or remuneration would be transferred to this bank account created by the employer. This is done as it is a more secure and convenient method of payment. However, it is not a mandatory requirement or an obligation on the part of the employer to create such bank accounts.
- Tax-related Documents: In ADGM, there is no personal income tax. However, employees may still need to comply with certain tax-related obligations, such as obtaining a Tax Registration Number (TRN) and filing relevant documents if they engage in business activities outside the ADGM jurisdiction. The ADGM Work Permit Guidance does not mention anything about the tax related documents as part of obtaining the work permit in the ADGM. It is advisable for the employees to consult their employer or relevant authorities if required, in order to get confirmation as to whether there are tax-related documents or requirements that they should comply with.
It is an obligation on the part of the employer to maintain the records of their employees during the employment as well as for a minimum period of 2 years after the termination of the employment. ADGM is a free zone that supports virtual documentation. Therefore, all the documents that are virtually submitted to the relevant authorities of the ADGM are also considered valid, for the purpose of employment.
Details on the documents required for the visa and work permit, along with the process and fee structure shall be detailed in the coming articles pertaining to ADGM Employment Regulations.
The above is the list of documents that are generally submitted to the relevant ADGM authorities. The ADGM authorities may seek any additional information or documents on a case–to–case basis.
REFERENCES:
- ADGM Employment Regulations 2019
- ADGM Work Permit Guidance
- ADGM Registration Authority Guidance
- https://www.adgm.com/faqs/search#what-is-the-basic-wage-